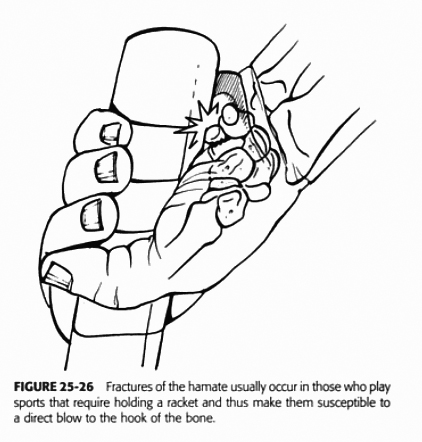
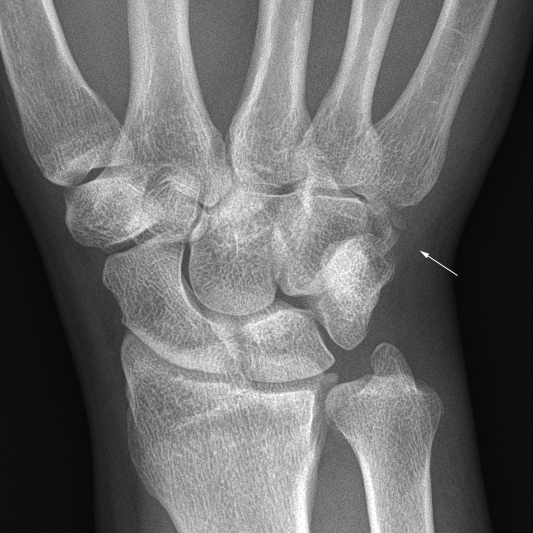
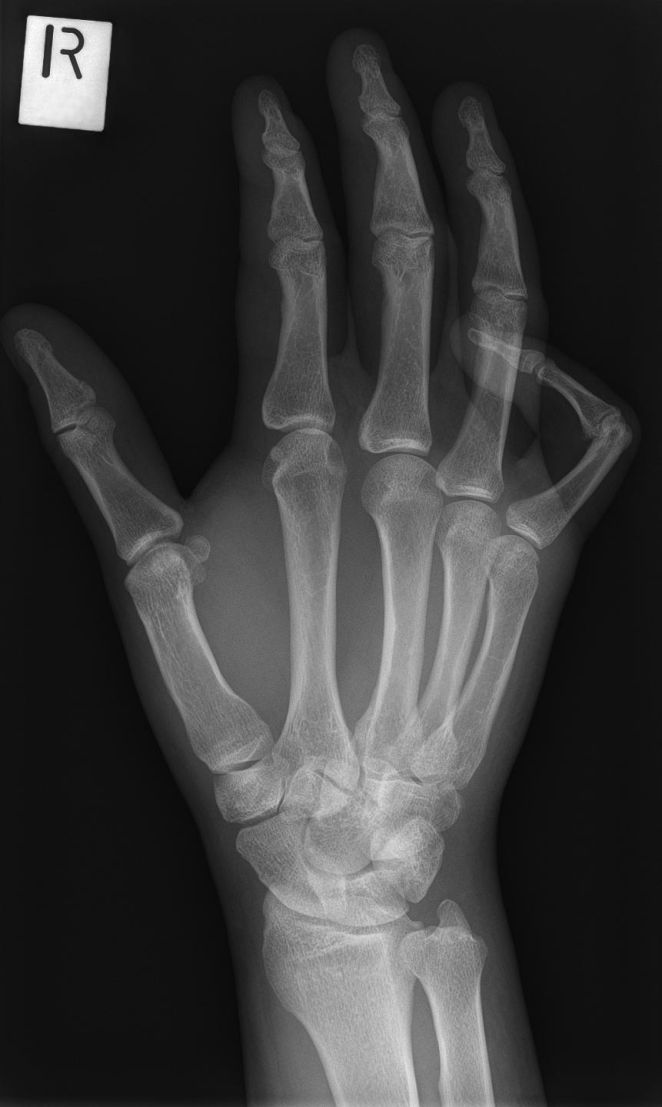
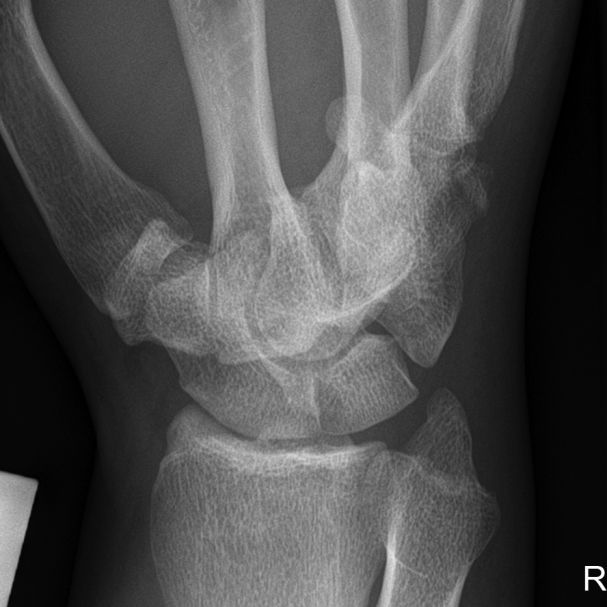
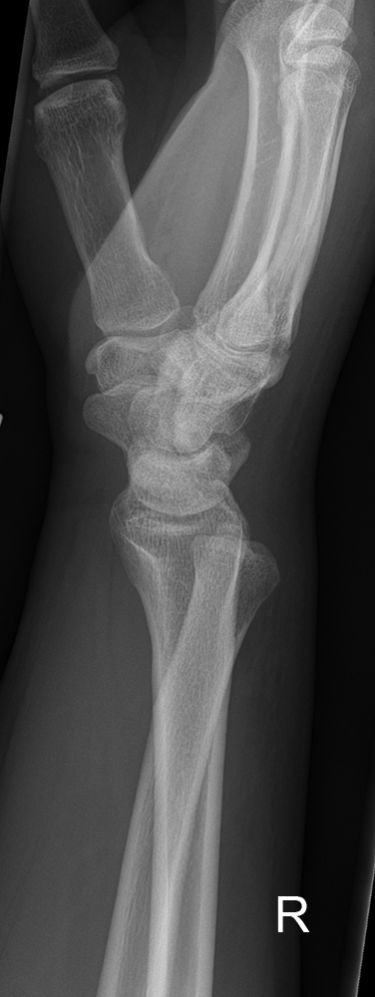
Imaging Hamate Fractures
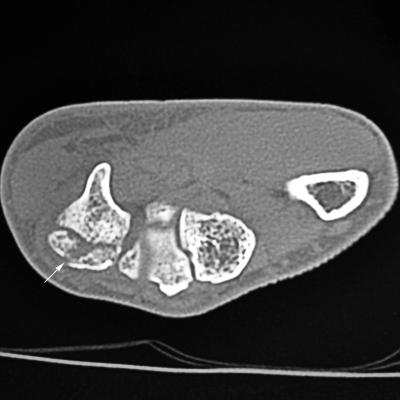
Hamate fractures are uncommon, comprising only 2 % of carpal bone fractures. <a class="external" href="http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/97813-overview" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">(http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/97813-overview)</a> Fractures of the hook of the hamate are more common than fractures of the body of the hamate. Hamate hook fractures are likely to be best demonstrated on the carpal tunnel view.
Anatomy
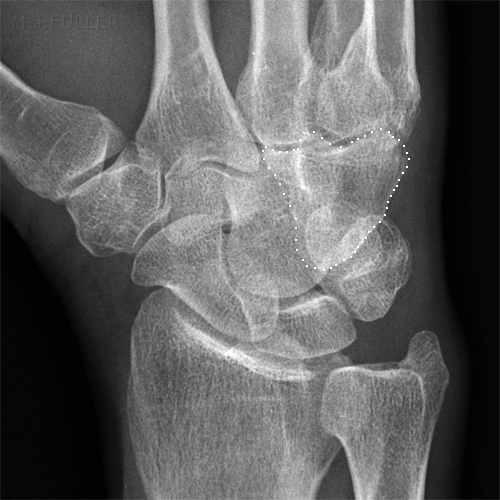
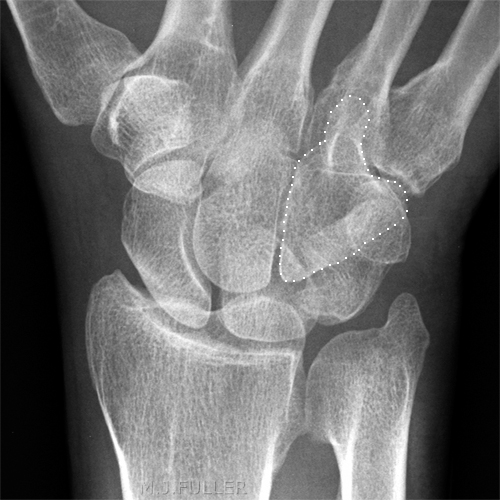
The hamate is the most ulnar carpal bone in the distal row. "The body of the hamate articulates distally with the bases of the 4th and 5th metacarpals, radially with the capitate and proximally with the triquetrum and lunate. The hook of the hamate (hamulus) is the distal border of Guyon's canal, which contains the ulnar artery and nerve. With injury of the hamate one should always assure vascular patency and that sensation is intact in the 5th digit and the ulnar border of the 4th. " (<a class="external" href="http://www.uptodate.com/patients/content/topic.do?topicKey=%7EuS6LlZ_xA/cJz6" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Kevin E. Burroughs</a>)
Mechanism of Injury
Fractures of the hook of the hamate are associated with sports injuries (golf, tennis etc) but may also result from a direct blow.
"Type I fractures involving the hook of the hamate are the most common and can occur via several different mechanisms.First, repeated microtrauma to the hook during sports involving swinging clubs, bats, or racquets can result in a hook stress fracture. These usually occur in the nondominant hand and account for approximately one third of hamate fractures.Second, direct trauma can be applied during sports when the butt of the club rests on the hamate and the force of the swing is then transmitted directly to the bone.In addition, indirect trauma can be applied to the hook through its muscular and ligamentous attachments.This can occur either when falling on a hyperextended wrist or during power grips.
Type II fractures involving the body of the hamate are less common than type I fractures and always require direct force.4 Most commonly, these fractures occur with a punch-press injury or dorsopalmar compression of the wrist between heavy weights"
<a class="external" href="http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/97813-overview" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Amy Powell, MD, Hamate Fracture, E medicine</a>
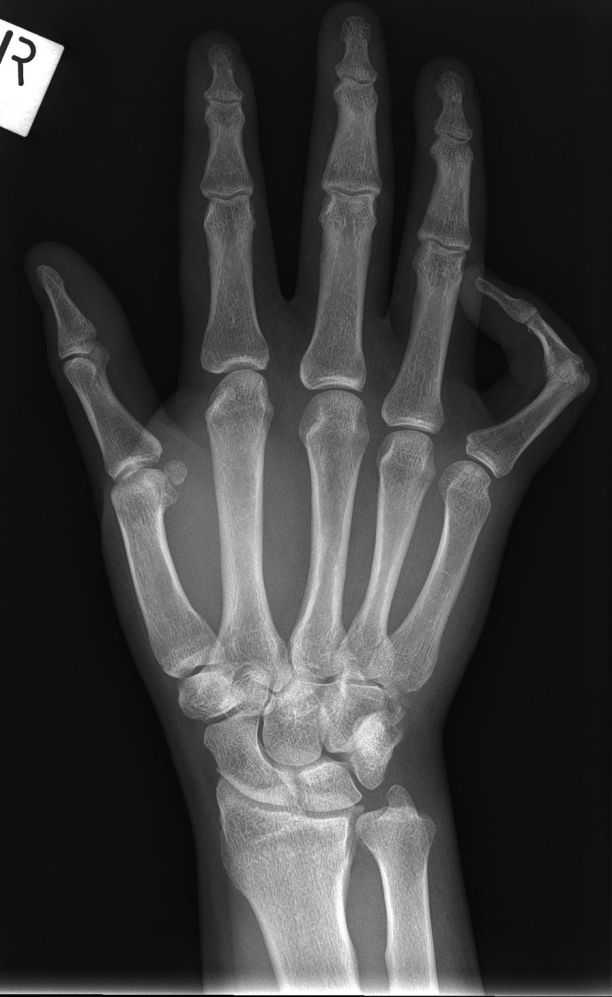
Radiography
Hamate fractures are not always demonstrated well on routine wrist views. A carpal tunnel view should be considered for hook of hamate fractures and a reverse oblique position can demonstrate hamate body fractures well
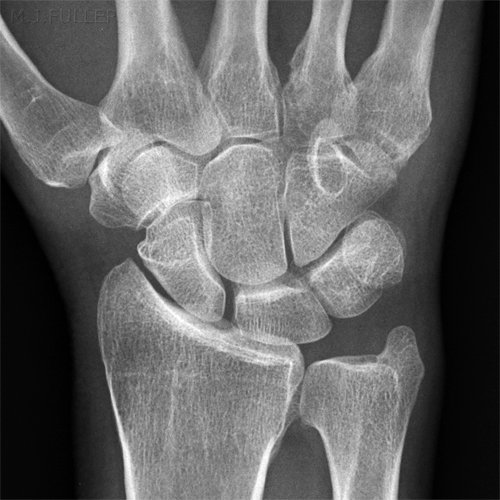
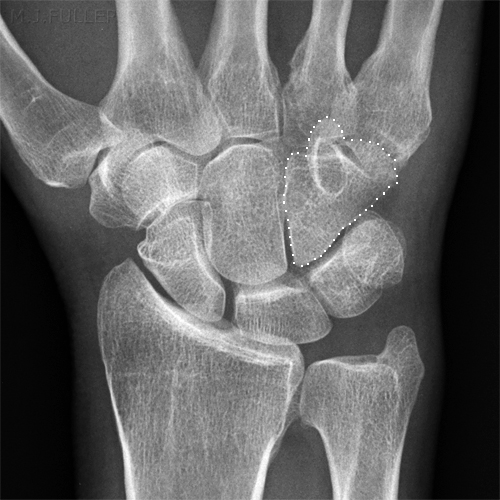
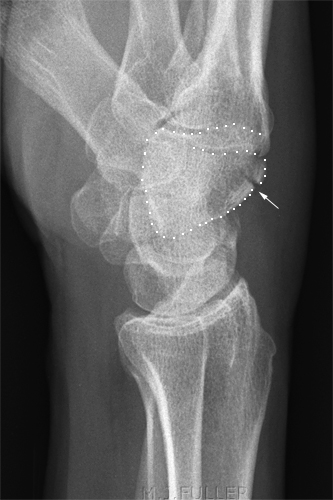
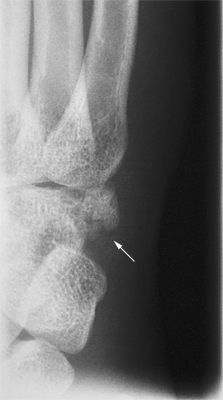
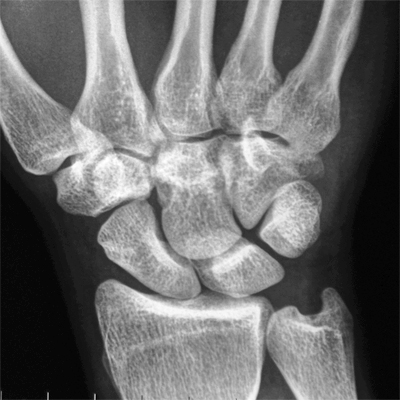
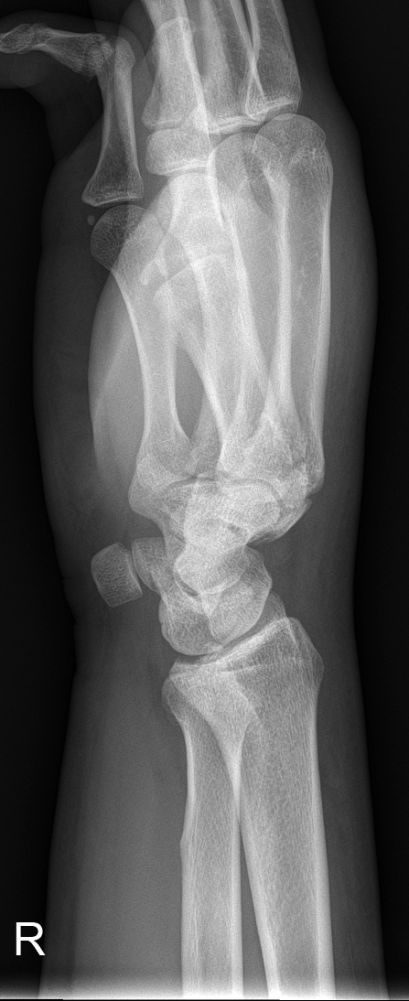
Case 1
This patient presented to the Emergency Department following an injury to his hand/wrist. The mechanism of injury is unknown.
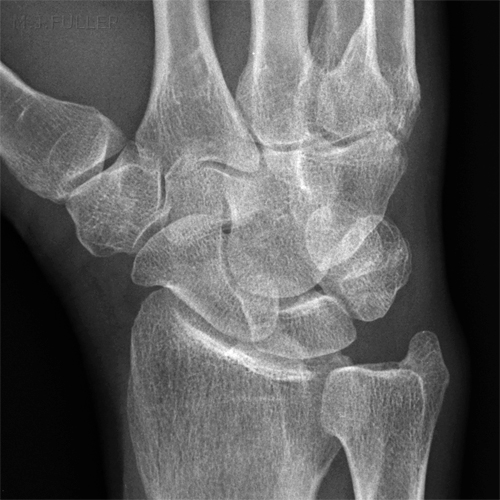
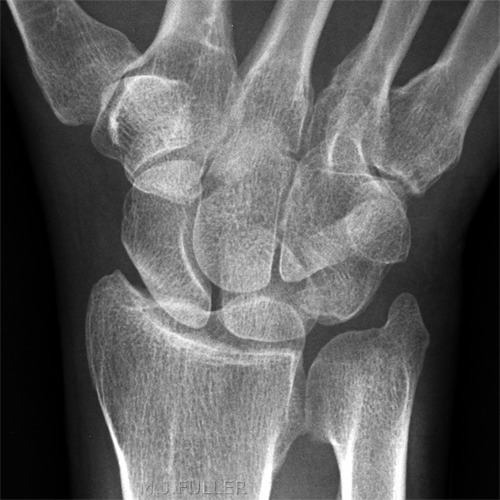
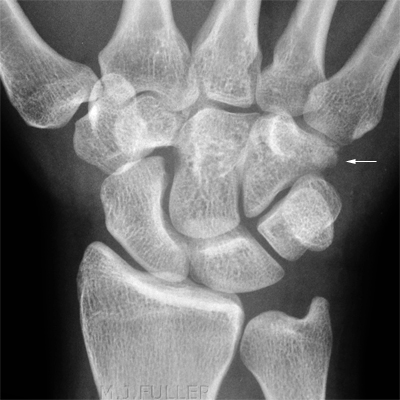
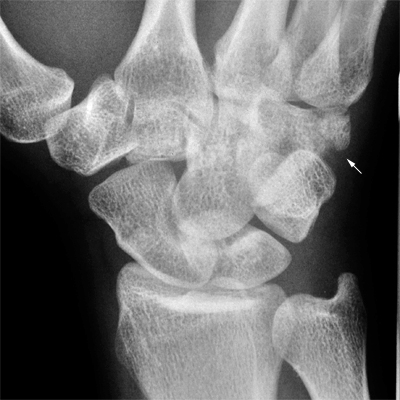
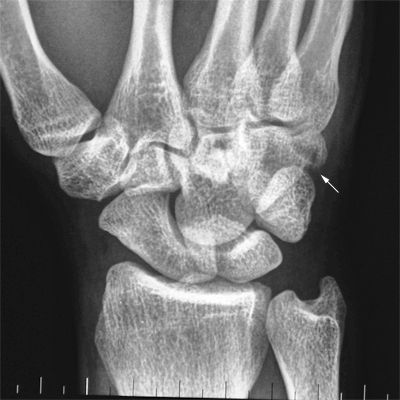
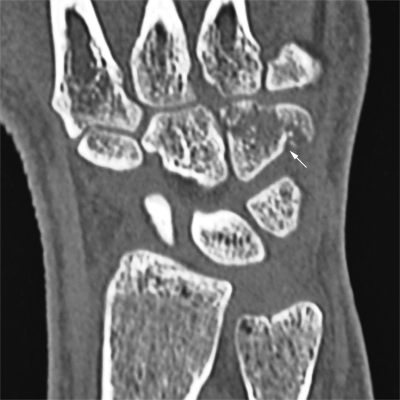
Case 2
This 34 year old man presented to the Emergency Department following an injury to his hand/wrist. The mechanism of injury is unknown.
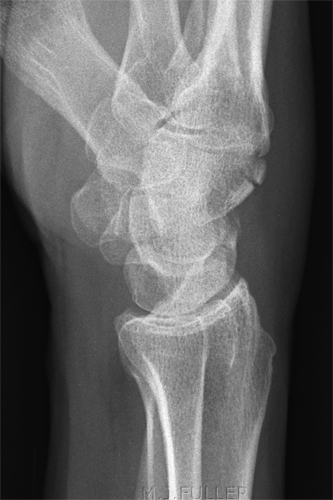
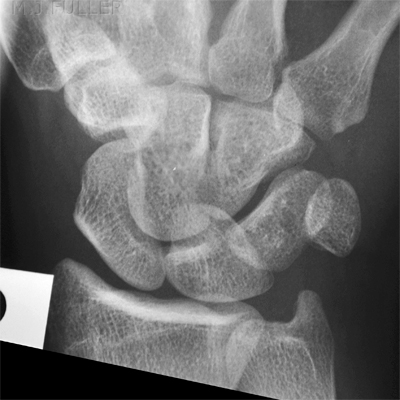
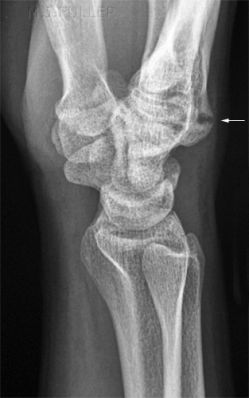
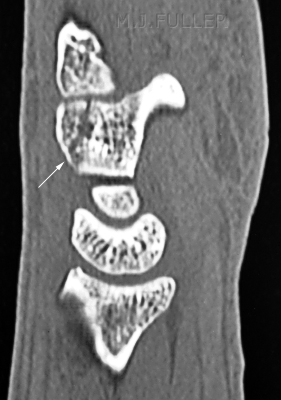
Case 3
...back to the wikiradiography home page
back to the Applied Radiography home page