Dacrocystography
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Introduction
Contra-indications
Anatomy
Preparation
Contrast or Subraction Artifact?
Nuclear Medicine Lacrimal Scan
Technique Notes
...back to the Wikiradiography home page
...back to the Applied Radiography home page
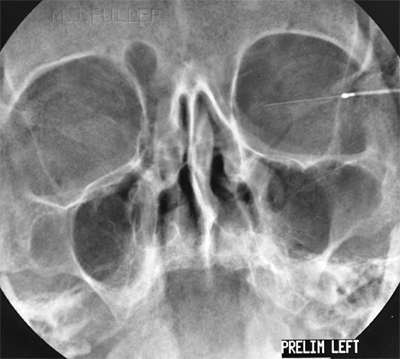
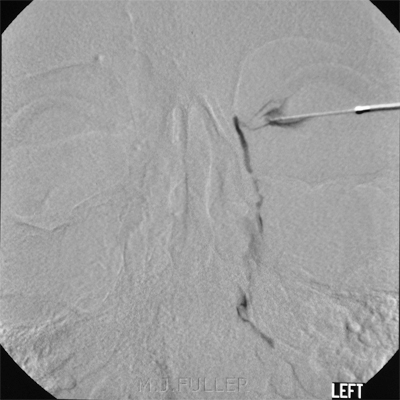
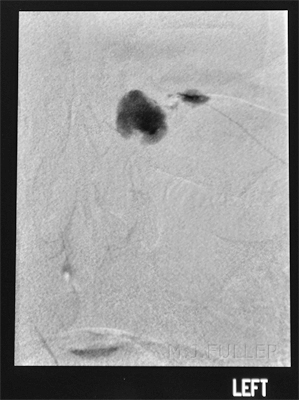
IndicationsA dacrocystogram is a radiographic examination of the nasal lacrimal duct(s) following administration of a contrast medium into the duct(s).
- Lacrimal duct obstruction/stricture
Contra-indications
- non-consent by patient to procedure
- contrast media or iodine allergy
- pregnancy (risk is minimal but patient may wish to delay procedure)
Anatomy
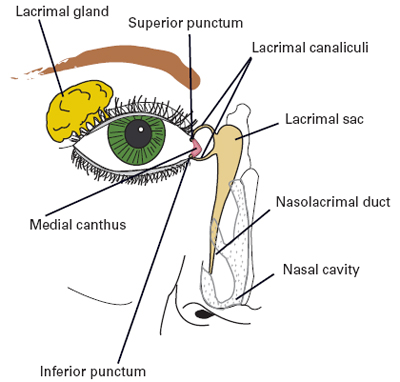
The American Journal of Managed Care, 14: S079-S087 <a class="external" href="http://www.ajmc.com/supplement/managed-care/2008/2008-04-vol14-n3Suppl" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">April 2008</a>Number 3 SupplTears (lacrimal fluid) are produced by the lacrimal gland which is located at the supero-lateral aspect of the orbit.
Drainage of the lacrimal fluid is achieved by the lacrimal canaliculi, lacrimal sac, and nasolacrimal duct. The lacrimal fluid drains from the nasolacrimal duct into the nasal cavity via the inferior meatus of the cavity.
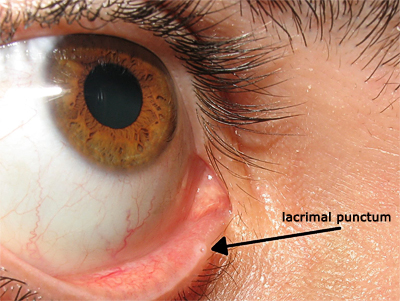
adapted from original photograph by <a class="external" href="http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lacrimal_punctum.jpg" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Diogo Melo Rocha</a>"The lacrimal canaliculi, one in each eyelid, commence at minute orifices, termed puncta lacrimalia (or lacrimal punctum, or lacrimal point), on the summits of the papillae lacrimales, seen on the margins of the lids at the lateral extremity of the lacus lacrimalis. There are two lacrimal puncta in the medial (inside) portion of each eye which in turn connect to the lacrimal sac."
<a class="external" href="http://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Lacrimal_punctum" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">(www.wikidoc.org)</a>
Preparation
- patient identification (3 'C's- correct patient, correct side, correct procedure)
- completed consent form
- no diet restrictions
- collect/review relevant previous imaging for ease of access prior to procedure
Technique
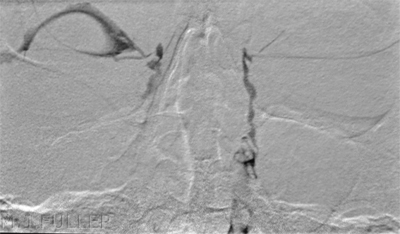
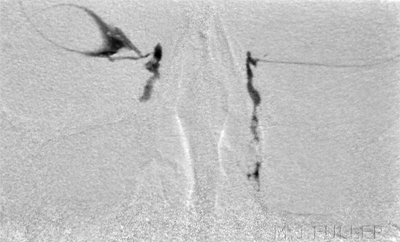
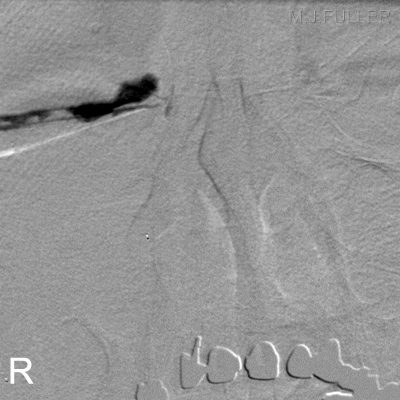
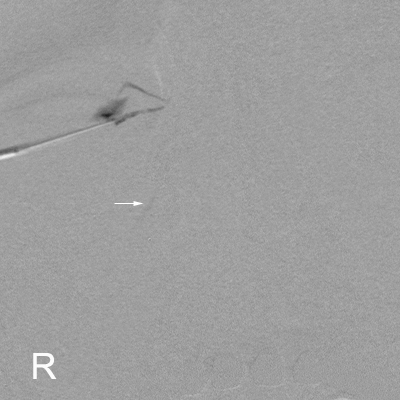
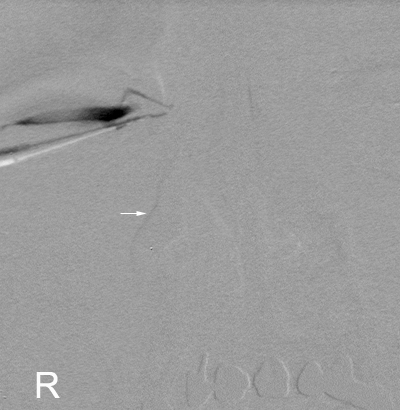
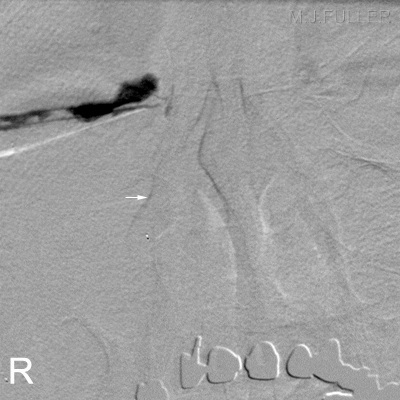
Contrast or Subraction Artifact?
It will not always be clear whether you have demonstrated contrast filling or subtraction artifact
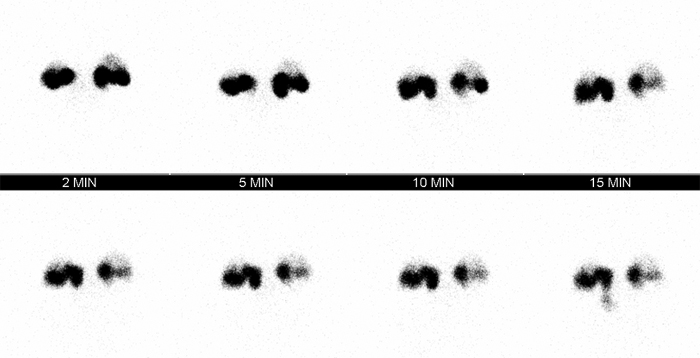
Nuclear Medicine Lacrimal Scan
Technique Notes
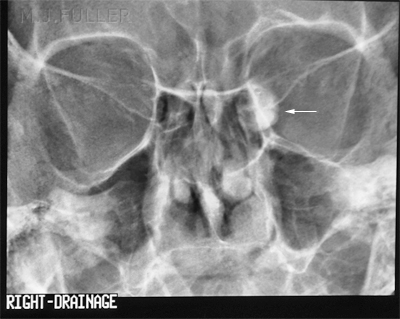
- The radiologist may choose to image the two sides separately- it is preferable to inject both sides at the same time
- It is normal practice to image the affected and unaffected sides.
- Collimate the X-ray beam to include the orbits superiorly and laterally and the maxillary paranasal sinuses inferiorly
- A sialogram needle (metal or plastic tip) can be used for cannulation of the puncta (16 gauge or similar)
- It is usually not tenable for the patient to hold their breath during the DSI subtraction acquisition sequence- with respiration, the effectiveness of the subtraction will vary
- If the patient moves during the acquisition sequence, it may be possible to select a new mask from the end of the sequence.
- Dacrocystogram protocol may include adjunct nuclear medicine study
- Maximum detail achieved with selection of fine focus (smallest focal spot size)
- A focused spotlight can be a useful aid for the radiologist in locating the lacrimal punctum
- inferior punctum is often easier to canulate
- catheter should not be inserted too far into the canaliculus- need to be able to see if the contrast refluxes out the other lacrimal canal.
...back to the Wikiradiography home page
...back to the Applied Radiography home page