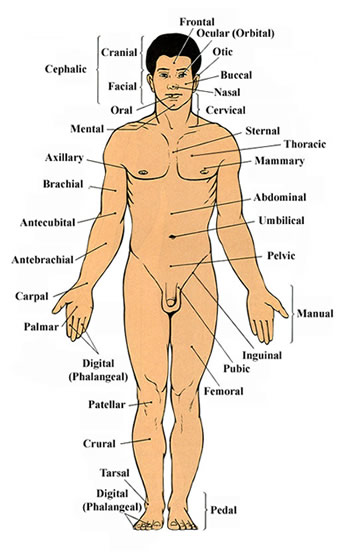
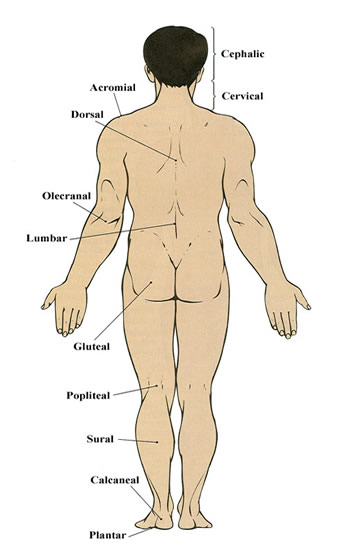
Anatomical Terms
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
A strong knowledge of anatomy is important in the study of radiography. Here is a list of body regions that you need to become familiar with: Anatomical Prefixes
Go Back to General Radiography Page | Other related pages of interest |