Radiography in the Round
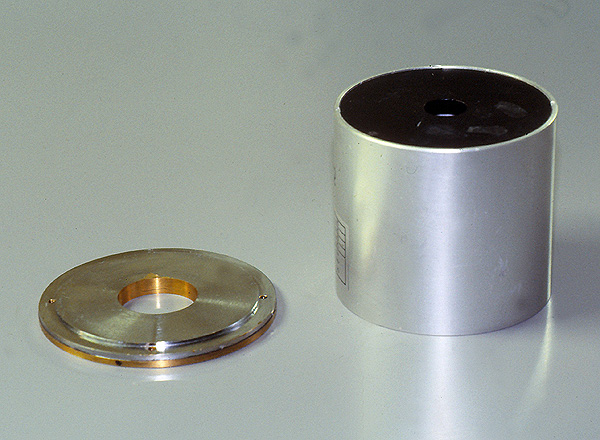
| | A round cone is a device that attaches to the light beam diaphragm to produce a radiation beam that is round in cross section. Round cones usually come in the form of an extension cone which has a primary cone and a secondary cone to "clean up the penumbra". |
| Round cone with secondary cone removed |
A round cone is a device that attaches to the light beam diaphragm to produce a radiation beam that is round in cross section. Round cones usually come in the form of an extension cone which has a primary cone and a secondary cone to "clean up the penumbra"
.
What are the advantages of Using a round Cone
The Science
Round cones reduce scatter radiation and reduce patient radiationdose. It is worth considering that the effect of the round cone is in three dimensions not two. That is to say, there is a volume of tissue that is not irradiated, not an area of tissue. When using a round cone you are effectively cutting off the corners of a radiation field.
The ArtThere is an aesthetic appeal with the round cone that is undeniable. It should be borne in mind that the form should not displace the function- there are certain anatomical regions that lend themselves to the use of the round cone. For example, anatomy that is basically round (eg lateral skull) lends itself to the use of a round cone. Conversely, anatomy that is characteristically square (CXR,AXR) would not be well suited to a round radiation field.
The use of a round cone does not prevent the use of the collimators of the LBD, indeed, many of the examples below use both methods of collimation.
The PoliticsRound cones can be used as a method of standardising coning. If your department protocol requires the use of a particular FFD and particular extension cone for, say, the lateral L5S1 view, the radiographers will be effectively standardising their coning.
The Disadvantages of Using Extension Cones
Radiographic Technique with Round Cones
- Extension Cones can be heavy. You will need to check that the weight of the extension cones do not void the warranty on new equipment
- Extension cones could pose a risk to your patient if they fall onto the patient. A quick release safety lead will reduce this risk considerably
- Introducing compulsory use of extension cones may require your radiographers to re-learn some radiographic techniques. This is a legacy of having to centre more accurately.
- If the extension cone is too small, it may result in a higher repeat rate
It is useful to have 3 sizes of cones. These typically correspond to anatomy as follows
- skull
- paranasal sinuses
- temporomandibular joints (TMJs)
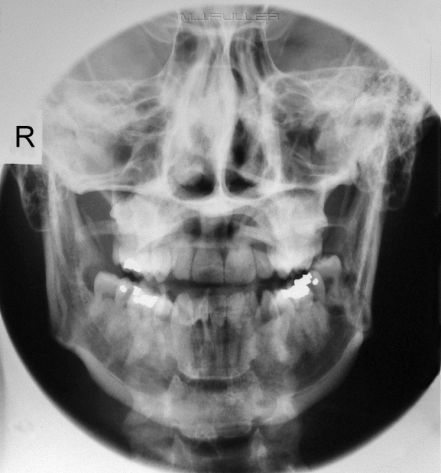
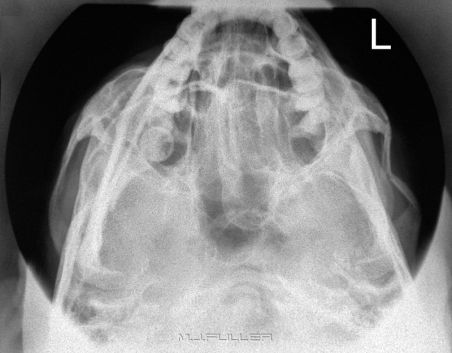
| | This is an AP mandible image using the sinuses cone and a butterfly configuration of 2 identical aluminium filters. Note that this is a radiograph not a digital image |
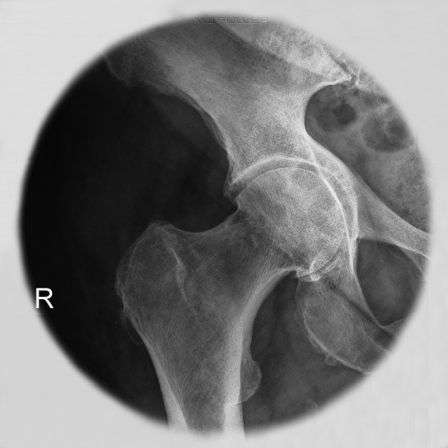
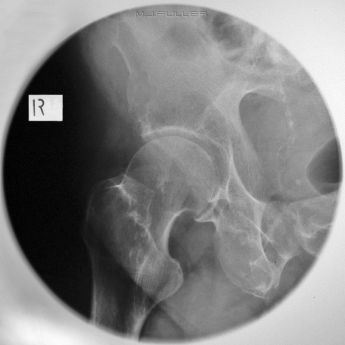
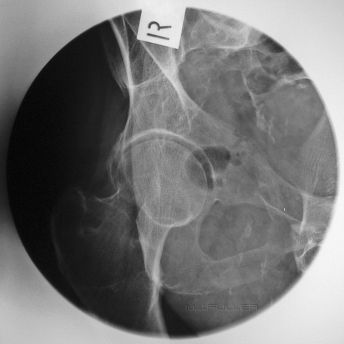
AP Hip
| | This is an AP coned hip radiograph of a patient with a suspected NOF fracture. The corners of this image are not required. The round cone reduces scatter radiation. |
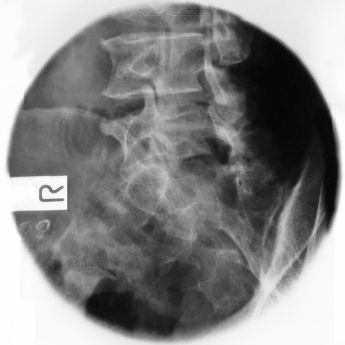
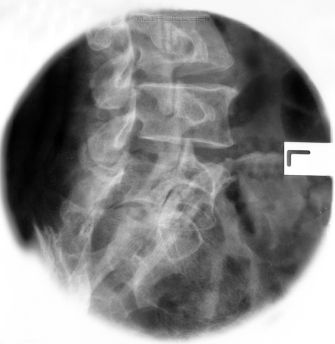
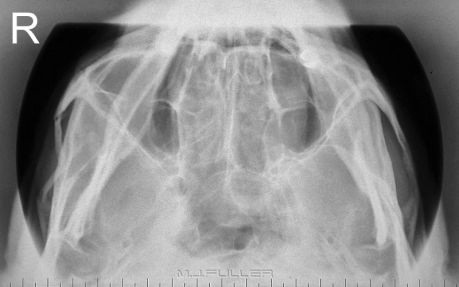
Oblique Lumbar Spine
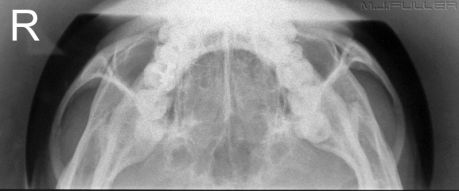
Judet's View of the Hip
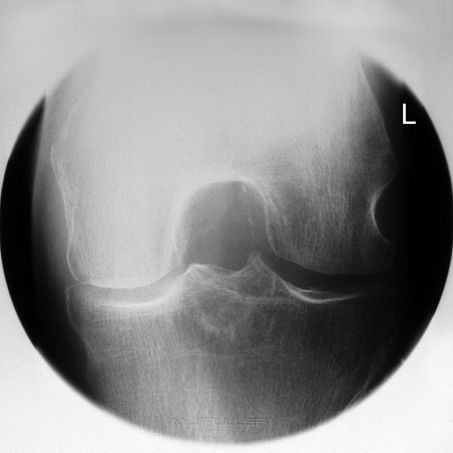
Intercondylar View of the Knee
Intercondylar view of the knee taken with the DARRIN positioning aid. search this wiki for more information on the DARRIN
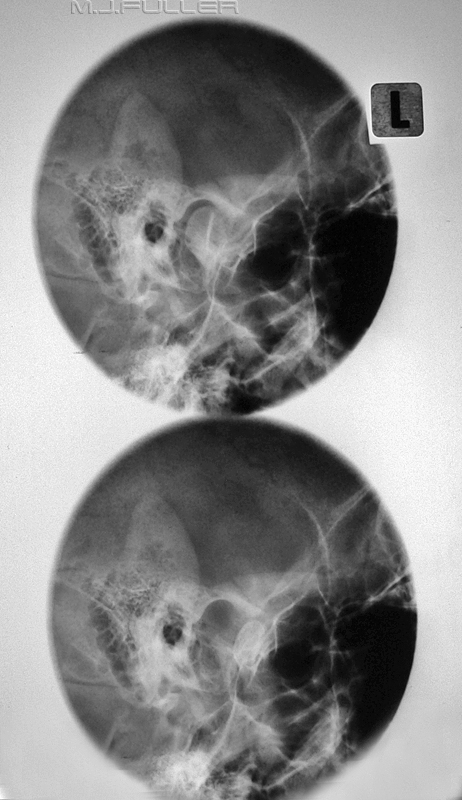
Slit Basal 1
| | Slit basal projection with round cone demonstrating a left comminuted and depressed fracture of the zygoma |
Slit Basal 2
| | Just to prove that the first one wasn't just serendipity...another one! |
Slit Basal 3
| | last one |
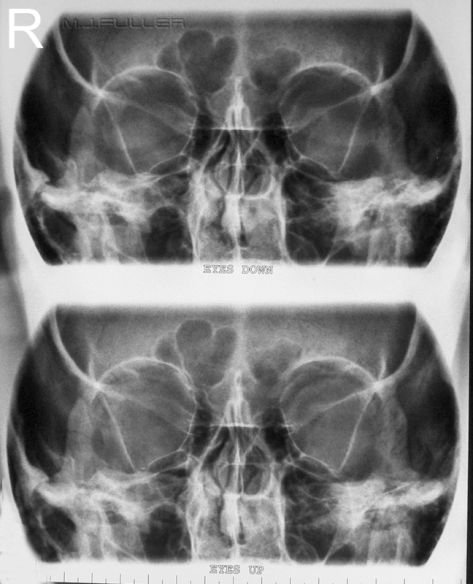
Orbits for Foreign Body
| | These images are PA 25 degree orbits. Both images are on the same film. This is achieved with a film displacement technique in the bucky. This is a digital image |
Lateral Oblique Temporomandibular Joints
| | These are open and closed mouth temporomandibular joint images. The patient's head is positioned in the true lateral position and a 25 degree caudal angle is used. Both images are on the same film using a cassette displacement technique |
Lateral Oblique Cochlea Implant
| | Similar positioning and technique to the lateral oblique temporomandibular joints. Note that this projection is circa 1980s and is possibly not in current favour to demonstrate a cochlea implant |
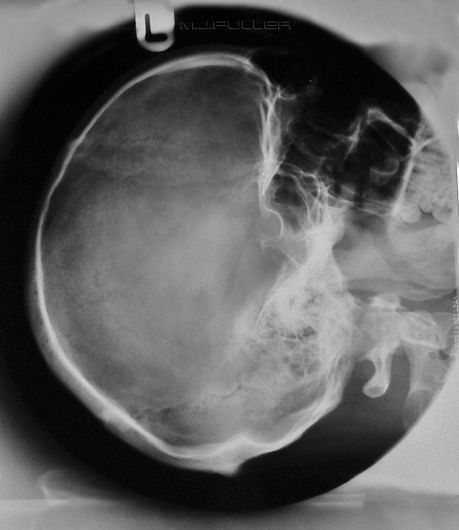
Lateral Skull
| | The lateral skull was perhaps the definitive application of the round cone |
Swimmers View of Cervico-thoracic Junction
| | Swimmers view often suffers from scatter radiation degradation. The round cone minimises scatter radiation. This is a radiograph not a digital image |
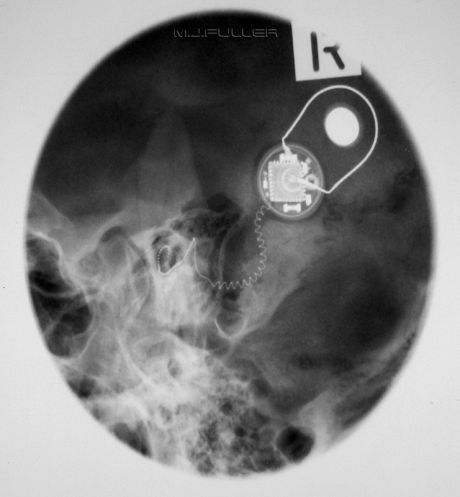
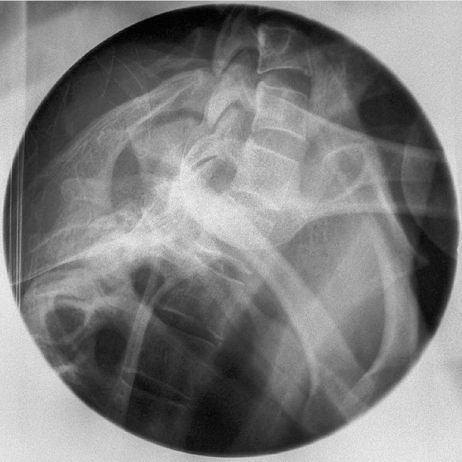
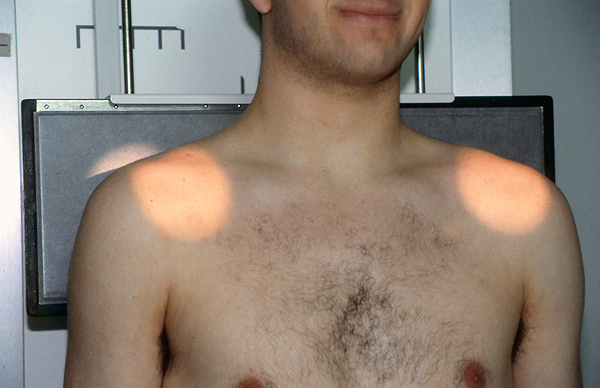
Binocular Cone for Acromio-clavicular joints
| | The binocular cone is a special purpose cone for acromio-clavicular joint imaging. In one exposure you can image both AC joints without primary beam exposure to the patient's thyroid. By varying the FFD the circles become larger and further apart. |
| |
| |
... back to the Wikiradiography home page