Radiography as a Career
What is a Radiographer?
The Radiographer is also know as radiologic technologists,diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology and work as part of a multidisciplinary health care team, having responsibility for the production of medical images to assist medical diagnosis and medical decision making. They play a pivotal role in selecting and implementing the most appropriate examination protocols which will answer the clinical question.
Medical images are created using X-rays, ultrasound and magnetic resonance. When producing medical images, radiographers must implement appropriate protection measures and act at all times to keep the radiation dose as low as practicable. Radiographers are obliged to act in an ethical and professionally responsible manner and exhibit a high level of communication skills. Radiographers work in collaboration with radiologists, and other specialist medical practitioners. They work in hospitals, clinics, medical laboratories, nursing homes, and in private industry.
Roles of a Radiographer
A Radiographer's primary role is to perform imaging as requested by referring doctors or specialists. This can include images while the patient is undergoing a surgical procedure in theatre with image intensifier (II) , in the Emergency Department (ED), in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), neonatal unit (NNU) while the patient is unconscious and ventilated, or as an outpatient where the patient is mobile.
A Radiographer may perform the following tasks:
- receive and interpret requests from medical practitioners for imaging examinations to be performed on patients
- determine the appropriate imaging techniques which will provide diagnostic information for the doctor
- calculate details of procedures such as length and intensity of exposure to radiation
- explain procedures to patients, and address any concerns they have about radiation
- ensure patients receive the correct preparation for the procedure
- correctly position the patient and imaging equipment to obtain the best image of the area being examined
- ensure the patient's welfare during the examination, including radiation safety
- post-process images or develop X-ray films
- check images after they are processed to determine if any further views are necessary
- operate special equipment such as
- fluoroscopy equipment (which gives a moving image of the part being examined)
- angiography equipment (which images blood vessels)
- computed tomography (CT) equipment - which gives cross-sectional images of the body using X-rays
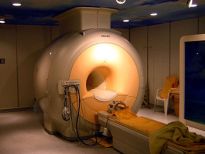
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment - which gives cross-sectional images of the body using magnets and radio-frequencies
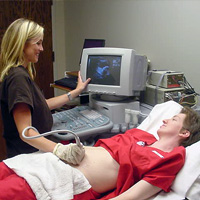
- ultrasound equipment - which images the body using soundwaves
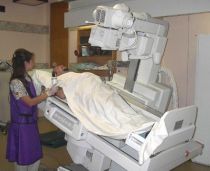
- mobile X-rays - produce general X-ray images using a mobile machine in varying locations throughout a hospital
- Image intensifier equipment - produce X-ray images in a surgical theatre
Modalities and Specialties
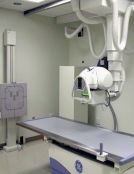
General Radiography Often called general or plain X-Rays and is the most commonly known and most frequently used form of medical imaging.
X-ray imaging is extremely fast and provides a rapid method of evaluating the entire body — especially the joints, bones and chest.
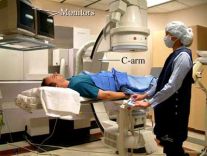
Angiography Angiography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins and the heart chambers. This is traditionally done by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy A fluoroscopy unit uses x-rays and an Image Intensifier to produce ‘real time’ 2D images, similar to a movie. Often, a contrast agent (barium or iodine) is used to make different body parts of the body more visible. Fluoroscopy can be used to examine the digestive tract, the kidneys and bladder, joints and to perform minor operative procedures such as intravenous line insertions.
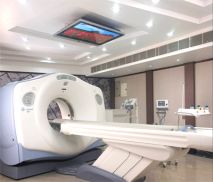
Computed Tomography CT CT is one of the more common modalities radiographers can specialise in. This is a method of imaging that produces "slices". This modality can easily image both the bone and soft tissue structures of the body, and with the assistance of contrast (X-Ray dye) clearly demonstrates the blood vessels.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI is another specialty for radiographers. This is one of the newest modalities in radiology. The images produced by an MRI are very similar to a CT but the MRI does not use ionising radiation to produce them. This field usually requires further study to be fully qualified to operate the MRI.
Ultrasound Ultrasound, or Sonography, is another highly specialised field of radiography. A Sonographer may need to have first worked for a few years as a Radiographer before they can return to University to study Ultrasound imaging. This is another field that does not use ionising radiation to produce its images, but instead uses sound waves. This is why it is most commonly used during pregnancy as it has shown no negative effect on the unborn child. Pregnancy scans are probably the best known scans, but ultrasound is able to image all the soft tissues of the body extremely well. Ultrasound can image arteries and veins as well as tendons and ligamants. Sloid organs such as liver gallbladder and kidney are wellseen, but gas in bowel limits imaging ( as gas scatters the sound waves).
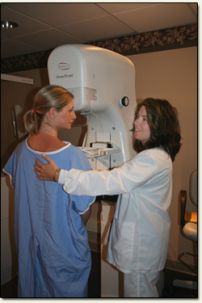
Mammography Mammography, or imaging of the breast, is a highly specialised field of Radiography. In the United States of America gender is not a consideration in choosing this as a speciality. However, in Australia it is usually only undertaken by female radiographers, and requires extra training and study to become a Mammographer.
Education
- In the United States, radiography training may be completed in a 2-year hospital based certificate program, a 2-year Associate of Applied Science Program; now <a href="https://www.argosy.edu/locations/twin-cities/health-sciences-1/associate-of-applied-science-in-radiologic-technology" target="_self">offline</a> and <a class="external" href="http://cahsonline.uc.edu/bachelor-radiation-science-technology/" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">online degree programs</a> are available, or as a four-year University based Bachelor degree program. Certification programs in additional modalities (Mammography, CT, MRI, bone densitometry, sonography) are available at many of the same institutions that offer the initial radiography training.
- In Australia, radiography is usually a 3-4 year university course. A list of the universities offering radiography is below. In most universities, it is called a Bachelor of Applied Science. The exception to both these rules is Monash University, which offers a 4-year Bachelor of Radiography and Medical Imaging course, and the University of South Australia which offers the 4-year Bachelor of Medical Radiation Science (Medical Imaging).
- Once the course is completed, graduates are "provisionally accredited" with the Australian Institute of Radiography, our governing body. Graduates must complete a qualification year to achieve full accreditation. In most states, this year is called the Professional Development Year (or PDY) is completed, although in VIC it is called an Intern Year and in QLD it is called the Foundation Year. During this year, the graduate radiographer is supervised by qualified radiographers to ensure they meet the required professional standard before they receive full accreditation.
- Sonographers gain their qualifications by returning to university. They can study either a graduate diploma or a masters in medical ultrasound.
Australian Universities offering undergraduate courses in radiography
NSW
- Charles Sturt University -<a class="external" href="http://www.csu.edu.au/courses/undergraduate/medical_imaging/index.html" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Applied Science (Medical Imaging)</a>
- University of Sydney -<a class="external" href="http://www.fhs.usyd.edu.au/mrs/fstudent/undergrad/index.shtml" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Appplied Science (Medical Radiation Science)</a>
- University of Newcastle -<a class="external" href="http://www.newcastle.edu.au/school/health-sciences/areas-of-study/mrs.html" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Applied Science (Diagnostic Radiography)</a>
VIC
- RMIT -<a class="external" href="http://www.rmit.edu.au/browse;ID=bg8tr5spivai" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Appplied Science (Medical Radiations)</a>
- Monash -<a class="external" href="http://www.med.monash.edu.au/bradmedimag/" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Radiography and Medical Imaging</a>
WA
- Curtin -<a class="external" href="http://handbook.curtin.edu.au/courses/30/309868.html" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Science (Medical Imaging Science)</a>
SA
- University of South Australia -<a class="external" href="http://www.unisa.edu.au/hls/progscourses/IBRS.asp" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Medical Radiation (Medical Imaging)</a>
QLD
- Queensland University of Technology -<a class="external" href="http://www.sci.qut.edu.au/study/courses/course-major.jsp?major-id=7192&parent-count=1" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Bachelor of Applied Science - Medical Radiation Technology (Medical Imaging Technology)</a>
Salaries
At the moment in Australia there is wide variance in the salaries for radiographers depending on the state in which you are working. It can also vary depending on whether you are employed in the private or public sector and just to complicate things more, the more qualified you are or if you have done a specialisation, you will receive a higher hourly rate.
Public Award 2008
NSW <a class="external" href="http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/resources/jobs/conditions/awards/pdf/hsu_he_medical_radiation_scientist.pdf" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">See award</a> VIC
QLD <a class="external" href="http://www.health.qld.gov.au/hrpolicies/wage_rates/hp_wagerates.pdf" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">See award</a> SA <a class="external" href="http://www.industrialcourt.sa.gov.au/download.cfm?downloadfile=5892AC89-E7F2-2F96-321DC96276C7795F" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">See award</a> NT <a class="external" href="http://www.ocpe.nt.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/48907/General_NTPS_2008.pdf" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">See award</a> WA
Below are short videos describing the field of Medical Imaging: