Proximal Tibiofibular Joint Dislocation
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Case 1
Introduction
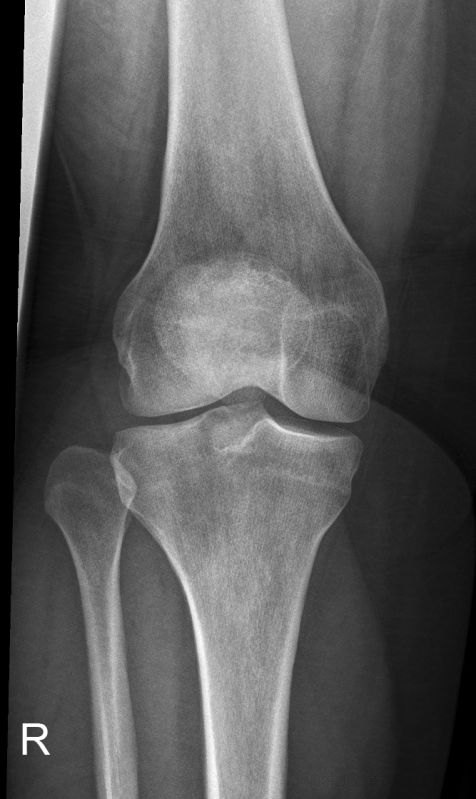
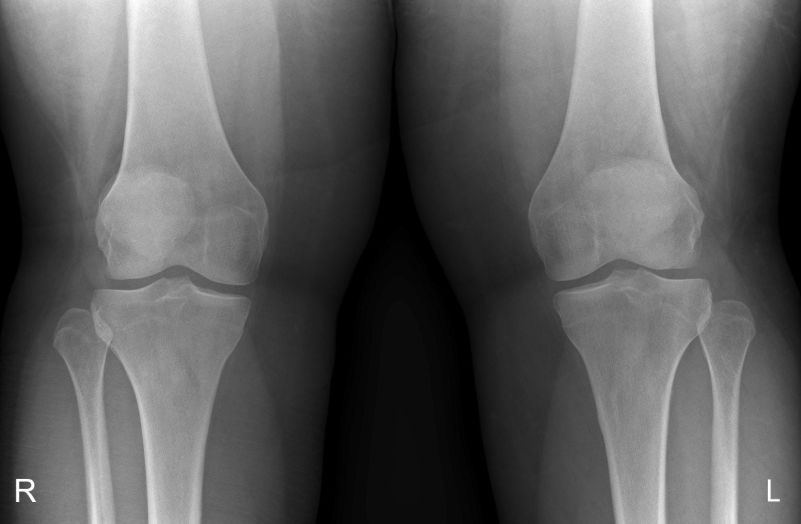
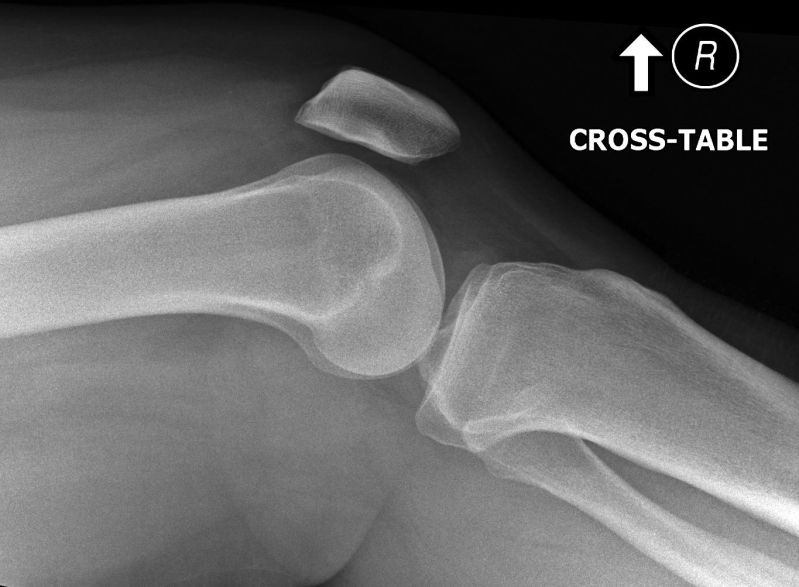
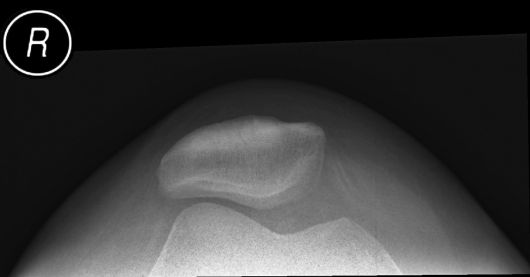
Proximal tibiofibular joint dislocation is more commonly referred to as a fibular head dislocation. This injury is uncommon but is worthy of attention because it can be easily missed and because it can be mimicked by a combination of other pathology and projectional factors.
Case 1