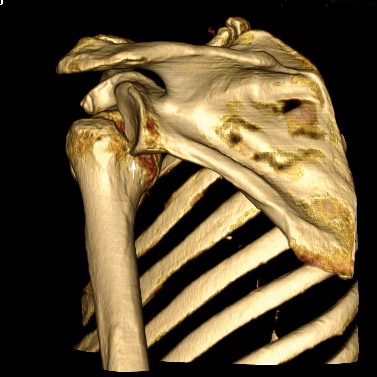
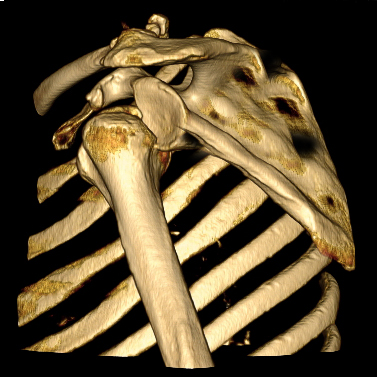
Hill-Sachs and Bankart Lesions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Introduction
Hill-Sachs Lesion
Radiographic Appearance
Case Studies
... back to the Wikiradiography home page
... back to the Applied Radiography home page
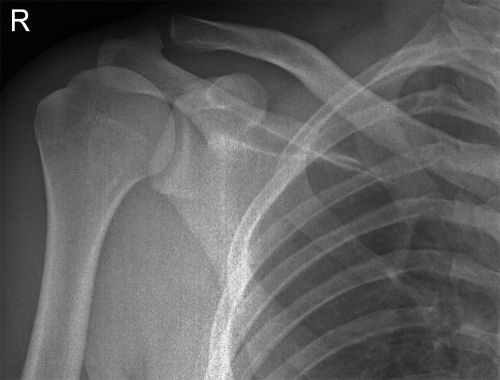
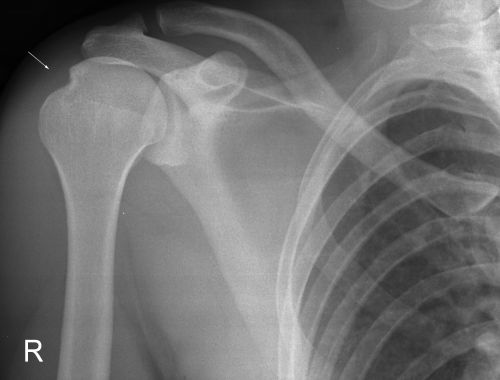
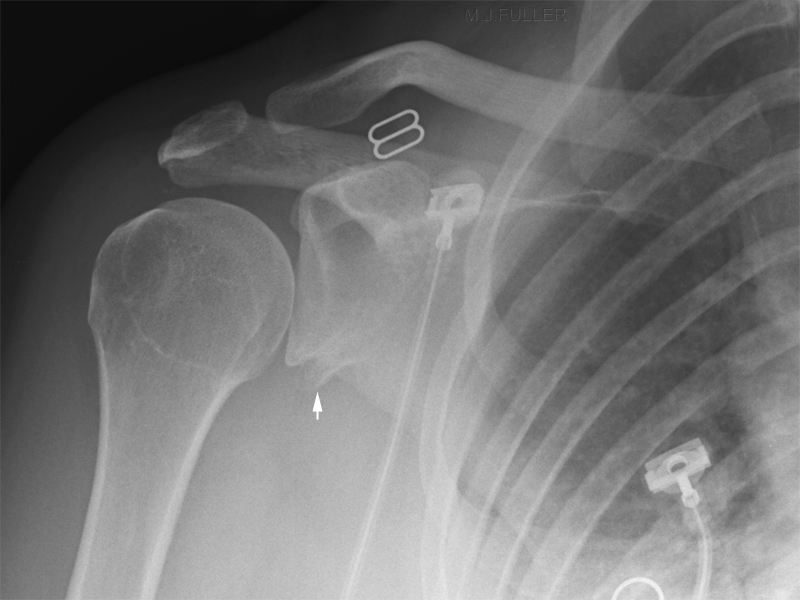
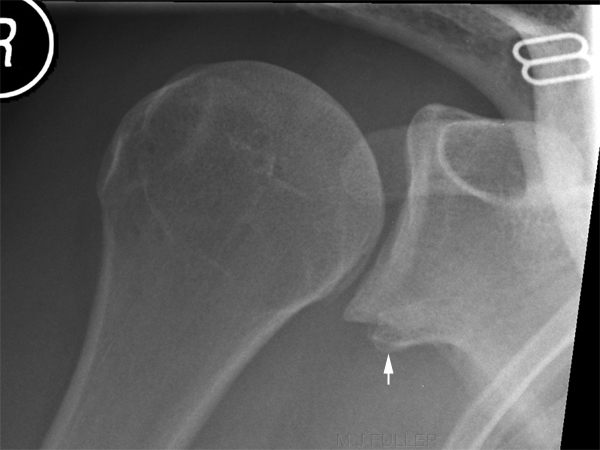
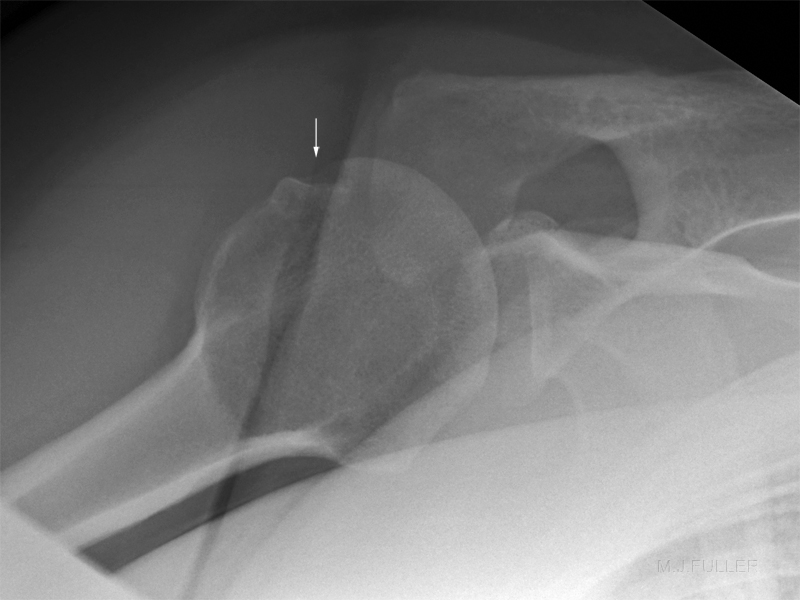
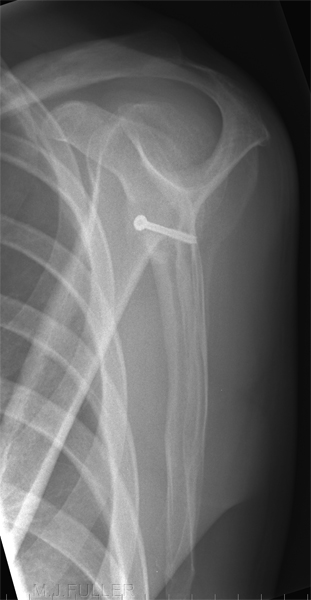
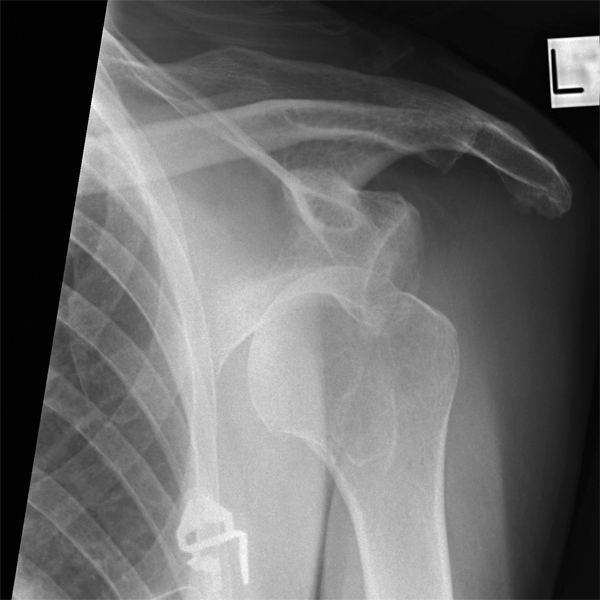
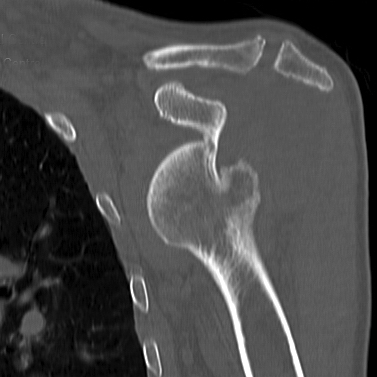
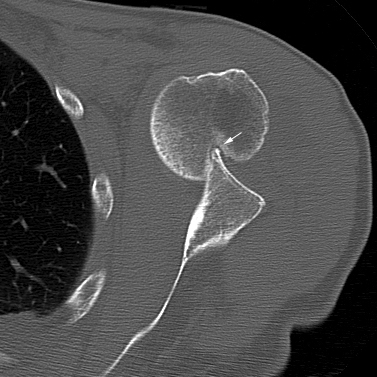
A Hill-Sachs lesion usually results from an anterior shoulder dislocation with resultant posterolateral humeral head compression fracture as the humeral head comes to rest against the anteroinferior part of the glenoid. It is often associated with a Bankart lesion of the glenoid.
Hill-Sachs Lesion
- A Hill-Sachs lesion occurs in more than 50 percent of patients with a primary dislocation.
- This lesion is associated with an increased risk of recurrent dislocation
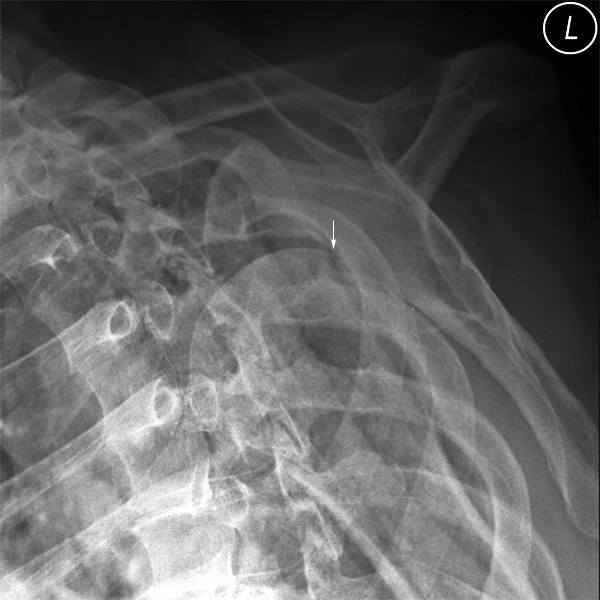
Radiographic Appearance
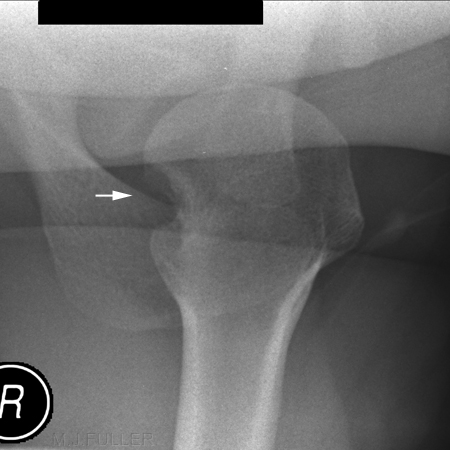
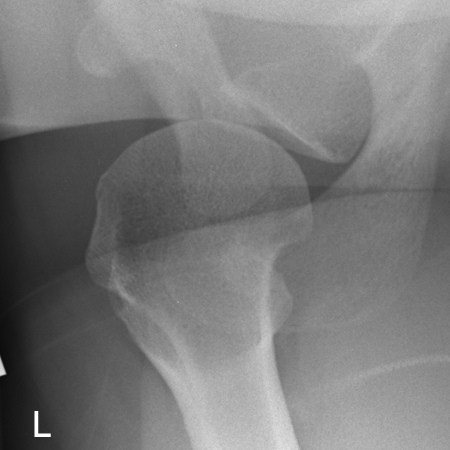
Hill-Sachs Lesion
Reverse Hill Sachs Lesion
Case Studies
Case 1
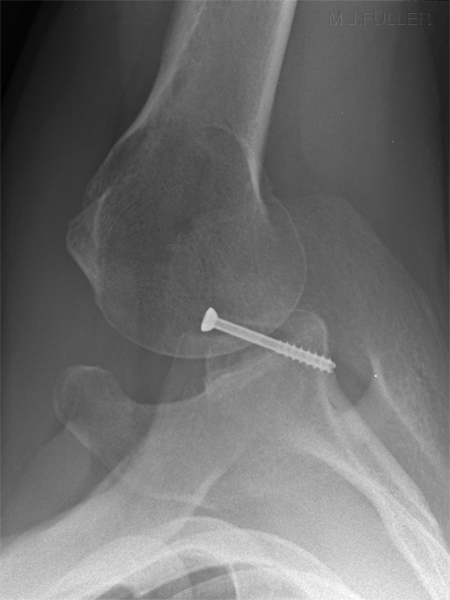
Case 2
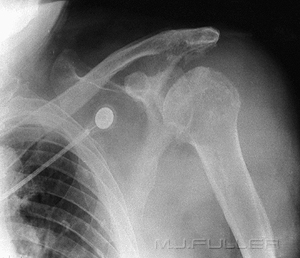
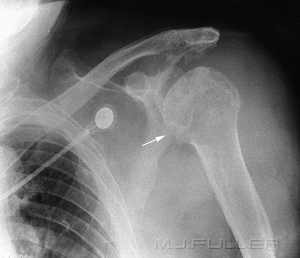
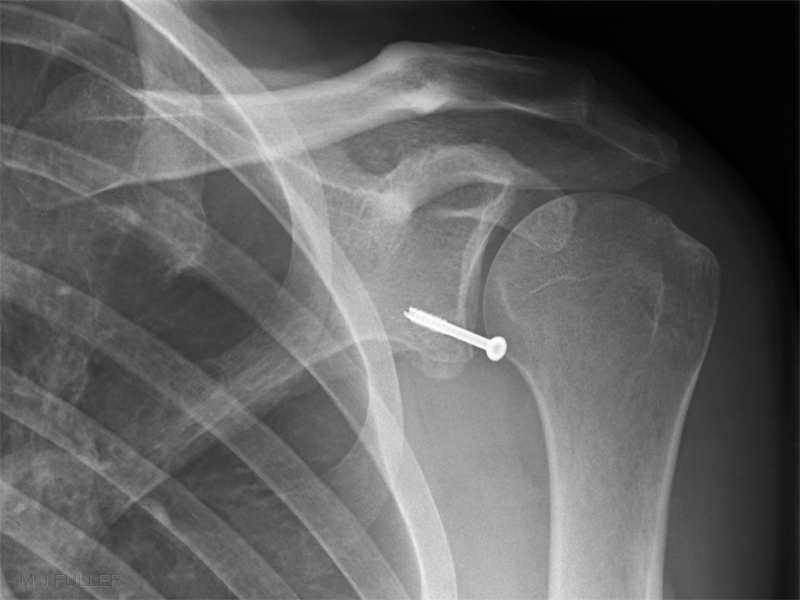
This patient has gad a surgical repair of a Bankart lesion
Case 3
Case 4
... back to the Wikiradiography home page
... back to the Applied Radiography home page