ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
AnatomyERCP is a fluoroscopic endoscopic procedure for demonstrating the biliary tree. ERCP can be performed anywhere that has a fluoroscopic facility. This would include operating theatres, endoscopy suites, angiography suites and fluoroscopy rooms. An understanding of the procedure will assist the radiographer to provide the best possible imaging service.
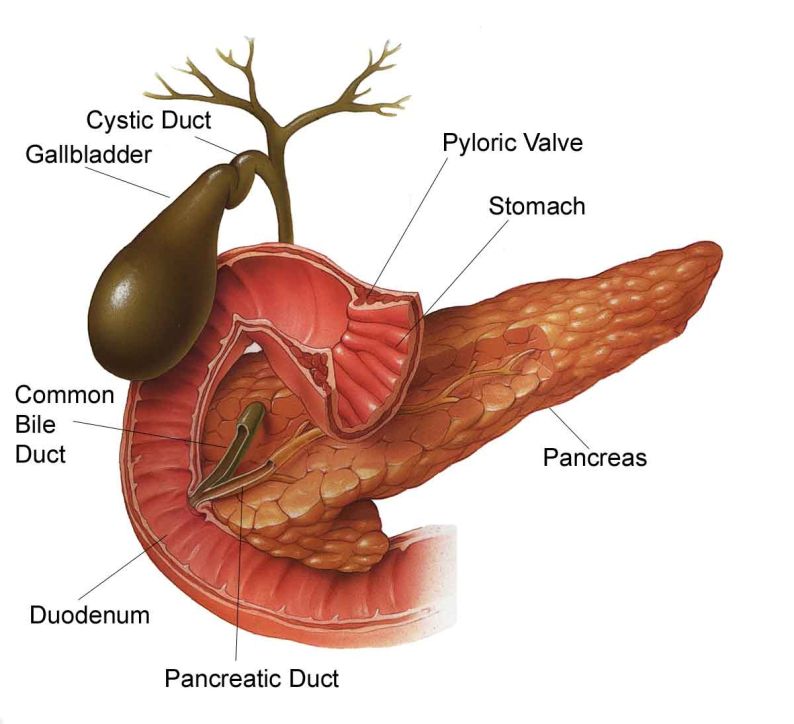
Biliary System Anatomy
<a class="external" href="http://gallbladder-symptoms.biz/WPC-edit-content/uploads/2010/10/GallBladder-Pancreas-02.jpg" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">
http://gallbladder-symptoms.biz/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/GallBladder-Pancreas-02.jpg</a> (28/2/2011)
The biliary system consists of the organs and ducts (bile ducts, gallbladder, and associated structures) that are involved in the production and transportation of bile. The transportation of bile follows this sequence:
1. When the liver cells secrete bile, it is collected by a system of ducts that flow from the liver through the right and left hepatic ducts.
2. These ducts ultimately drain into the common hepatic duct.
3. The common hepatic duct then joins with the cystic duct from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct, which runs from the liver to the duodenum (the first section of the small intestine).
4. However, not all bile runs directly into the duodenum. About 50 percent of the bile produced by the liver is first stored in the gallbladder, a pear-shaped organ located directly below the liver.
5. Then, when food is eaten, the gallbladder contracts and releases stored bile into the duodenum to help break down the fats.
Functions of the biliary system:
The biliary system's main function includes the following:
* to drain waste products from the liver into the duodenum
* to help in digestion with the controlled release of bile
Bile is the greenish-yellow fluid (consisting of waste products, cholesterol, and bile salts) that is secreted by the liver cells to perform two primary functions, including the following:* to carry away waste
* to break down fats during digestion
Bile salt is the actual component which helps break down and absorb fats. Bile, which is excreted from the body in the form of faeces, is what gives faeces its dark brown color.
<a class="external" href="http://medicalcenter.osu.edu/patientcare/healthcare_services/liver_biliary_pancreatic_disease/biliary_system_anatomy/Pages/index.aspx" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">Quoted from The Ohio State University Medical Center (28/2/2011)</a>
Relevant Videos
<embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/9bb40e8b5cb40ef6714d6d99d173cb336d3dcae8" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> <embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/620b4758bba67ae255a77f989d597aa5ca20da5a" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> <embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/e804ab15fc902781796b792d21e34132342db3e9" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> <embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/96e92d186b81fee71a20765286e5cb911fd1a0aa" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> <embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/43875e02a4c83347339b40fbd5bfe7d18961c310" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> <embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/33074870fc99e3ed85129eee20d00f77761e5fc2" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/>
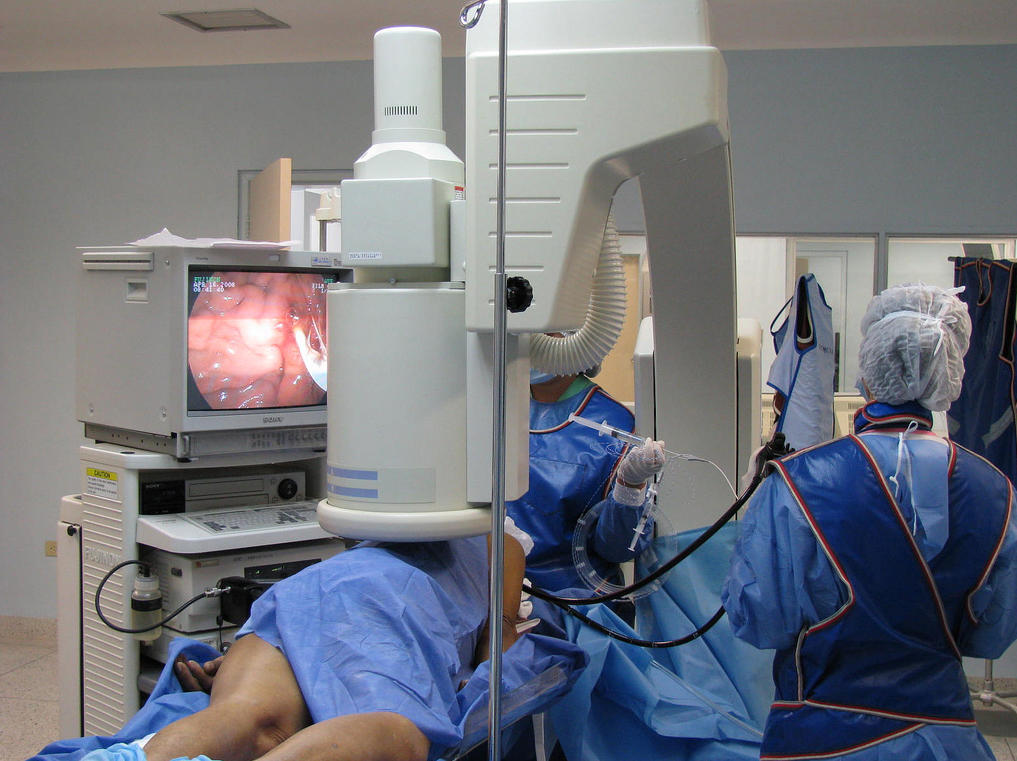
Technique
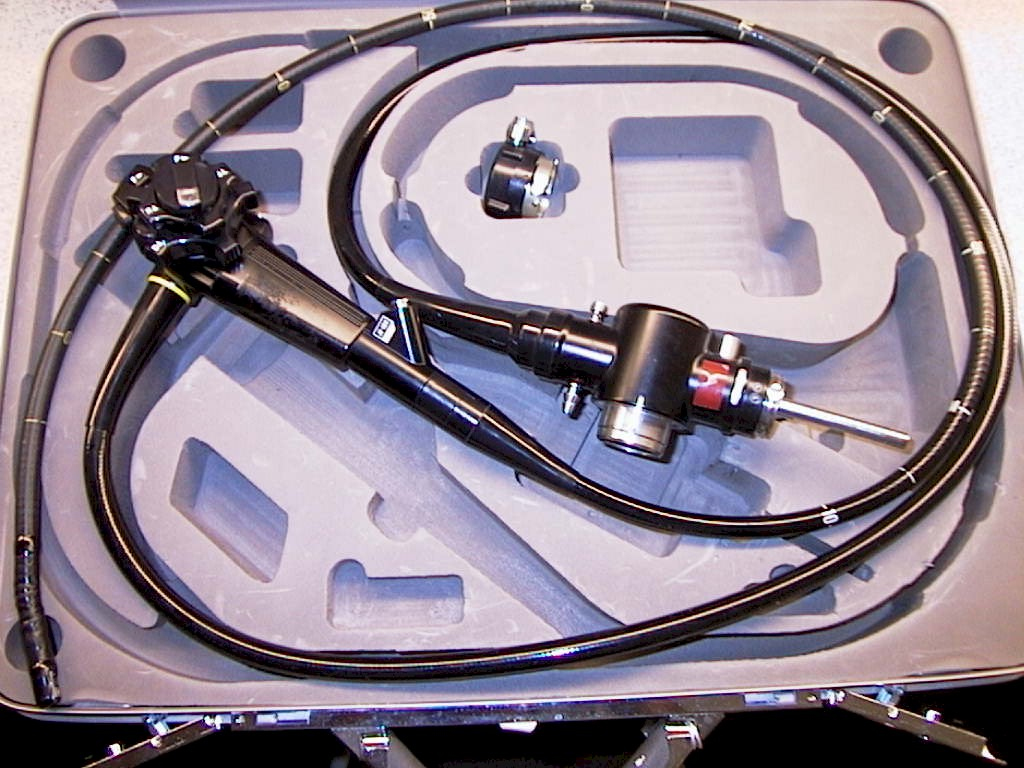
<a class="external" href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/21974686@N03/2447812991#/" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">http://www.flickr.com/photos/21974686@N03/2447812991#/ (3/3/2011)</a>You will be operating a fixed or mobile fluoroscopy unit at the direction of the endoscopist. There will be a nurse assisting the endoscopist, a scout nurse, an anaesthetist and an anaesthetic nurse. <a class="external" href="http://www.1800endoscope.com/endoscopes/duodenoscopes/JF100.htm" rel="nofollow" target="_blank">
http://www.1800endoscope.com/endoscopes/duodenoscopes/JF100.htm (3/3/2011)</a>The endoscope will look something like this. It has several attachments including suction and saline wash.
Technique Tips
- It is worth getting in early to set up the image intensifier- being called in at the last moment can cause problems
- It is necessary to establish whether the patient is pregnant before you start- no-one else may have considered the possibility
- It is important to identify the patient- you can't just pick up a request form lying on a bench in the room and assume it is the patient on the table. Ask the anaesthetist to identify the patient.
- Placing the image intensifier screen next to the endoscopy screen will help the endoscopist considerably.
- Before starting an acquisition sequence, undertake low dose fluoroscopy to centre the anatomy on the image. Landmarks can be hard to identify- look for ribs, iliac crests, lungs (the liver is on the right and below the diaphragm and above the iliac crests!)
- Sequence acquisition is superior to static images.
- Angle the beam to project the common bile duct off the patient's spine.
- Position the image intensifier with the X-ray tube under the table and with the image intensifier as close to the patient's skin as possible to increase field of view and decrease radiation dose. You may need to ask the anaesthetist to raise the table.
- You can engender a sense of camaraderie, common purpose and team work by helping with the patient transfers.
- If possible, load the sequence acquisitions to PACS to facilitate dynamic viewing of the study.
- It can be useful to wait for the operators report on the ERCP and include this when uploading to PACS.
Case 1
<embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/25c4dfa91d1ad31a565eb2e8b5808859f8577f08" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> This 88 year old male was referred for ERCP following diagnosis of gallstones on ultrasound imaging. A balloon catheter was inserted into the bile duct and positioned distally. The balloon was inflated creating a sealed system and contrast medium was injected into the bile duct. The contrast injection into the bile duct shows multiple filling defects.
If you click on the you tube logo you can watch this video at full resolution. You will need to select 720p and the fit-to-screen buttons to see the video in full resolution.Select the Esc key on your keyboard to return to normal viewing.
<embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/152df91fee6ffaebf8fd44c0c4e5bb6460325091" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> The balloon burst releasing airbubbles into the bile duct. Subsequent runs were marred by the presence of airbubbles.
If you click on the you tube logo you can watch this video at full resolution. You will need to select 720p and the fit-to-screen buttons to see the video in full resolution.Select the Esc key on your keyboard to return to normal viewing.
<embed allowfullscreen="true" height="350" src="http://widget.wetpaintserv.us/wiki/wikiradiography/widget/youtubevideo/b958d63aa35f4305ce1aefd424d7519a3020860a" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" width="425" wmode="transparent"/> A larger 20mm diameter balloon was inserted into the proximal bile duct, inflated and withdrawn all the way to the deuodenum. A gallstone was seen to enter the deuodenum on the endoscopic image.
If you click on the you tube logo you can watch this video at full resolution. You will need to select 720p and the fit-to-screen buttons to see the video in full resolution.Select the Esc key on your keyboard to return to normal viewing.